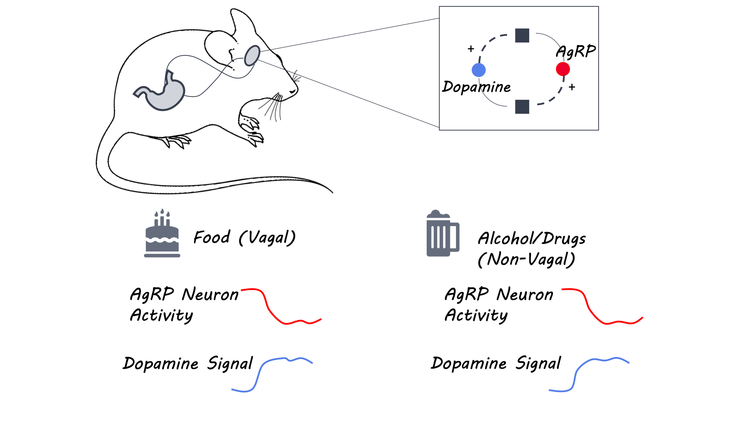
The motivation for natural rewards is mediated by both classic homeostatic circuits as well as mesolimbic dopaminergic circuits in the brain. It is not known how external rewards influence homeostatic circuits in the hypothalamus to alter behavior. Within the hypothalamus, agouti-related protein (AgRP-) and pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC)-expressing neurons play a key role in the control of food intake.
Published by BrainPost.